In December, the Census Bureau announced that the U.S. population had grown by nearly 1% in the year ended July 1st, 2024, marking the strongest annual gain since 20011. Given this, it seems strange to be already talking about slowing population growth. However, the reality is that the gap between births and deaths is continuing to shrink, with almost all of our recent population growth coming from immigration. Going forward, if immigration is dramatically curtailed, overall population growth could turn negative by the middle of the next decade while the working-age population would immediately start to contract.
For investors, it is important to consider all of this. An America with less population growth would see weaker demand growth overall but particularly for housing and basic consumer goods and services. Moreover, if the working-age population begins to fall well before the overall population, supply would be hit more than demand, potentially boosting wages, inflation and interest rates but also motivating even stronger investment in productivity-enhancing AI and robotic technologies.
The Tipping Point for Natural Population Growth
One way to assess this rather dramatic change in the demographic outlook is to look at natural population growth, that is births minus deaths, and net migration separately.
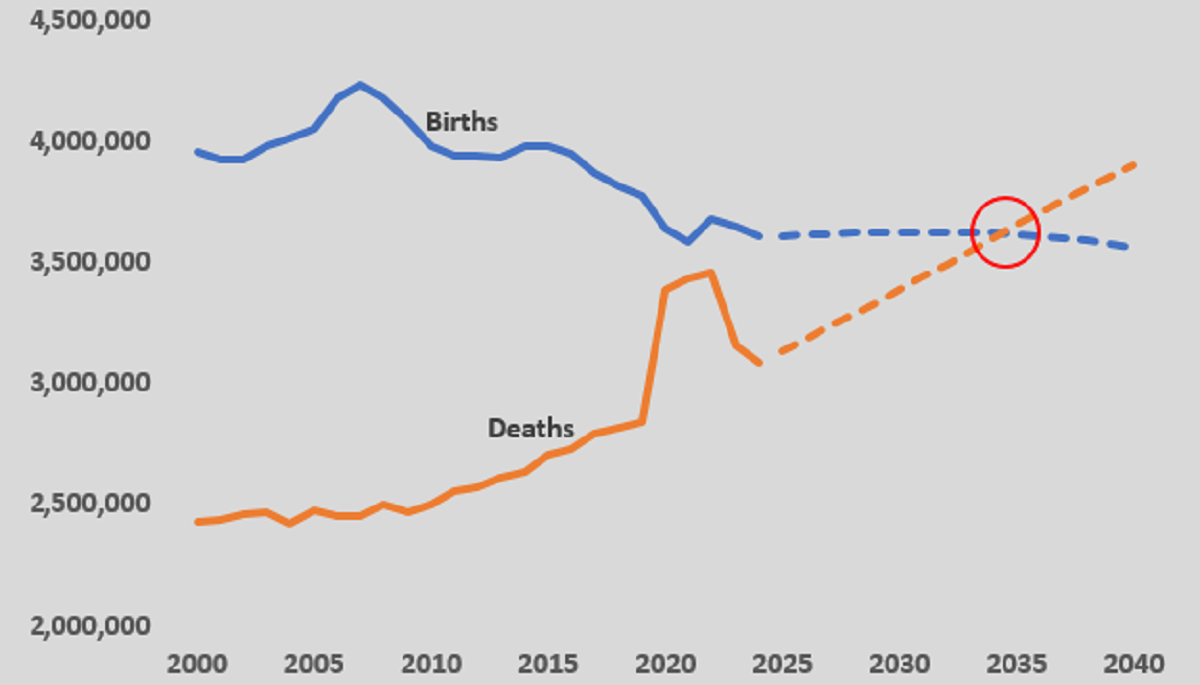
At first glance, the number of babies born in the United States appears fairly stable, ranging from 3.2 million to 4.5 million every year since 19502. However, this needs to be considered relative to the size of the overall population. In 1962, at the peak of the baby boom, almost 4.4 million babies were born in a population of just over 180 million people. Last year, in a population of 340 million, just 3.6 million babies were born.
So why has the birth rate fallen so dramatically? The answer is partly social and partly economic.
From a social perspective, the second half of the 20th century saw a dramatic increase in female participation in higher education and the labor force. In 1970, 42% of the undergraduates in U.S. universities were women. Last year, an estimated 58% were3. In 1970, the female labor force participation rate was 43%. Last year it was 58%. While these numbers reflect progress towards a more equal society, they have, not surprisingly, coincided with fewer and later marriages and smaller families.
From an economic perspective, a rapid increase in the cost of housing has absorbed many of the gains from two-income households while the cost of daycare, in particular, has made it extremely expensive for young couples to have children, further limiting births. Apart from some swings during the pandemic, crude birth rates have continued to decline and Census Bureau projections released in November 20234, adjusted for actual outcomes in 2023 and 2024, suggest that this will continue, with the raw number of births staying close to 3.6 million into the 2030s, even as the overall population, at least for a while, continues to rise.
Meanwhile, since the mid-1970s, mortality has continued to rise roughly in line with population, with the aging of the population offsetting significant medical advances, particularly in the area of heart disease.
There are, of course, many things that we all should do in reforming our lifestyles that could collectively reduce mortality. However, assuming such a reformation is not at hand, mortality will, sadly, steadily increase. Excluding the pandemic, the number of deaths has been on a steady upward trend: 2.4 million in 2004, 2.6 million in 2014 and 3.1 million in 2024. Again Census Bureau projections, adjusted for actual outcomes in 2023 and 2024, suggest that this pattern will continue with deaths, at 3.6 million in 2035, exceeding births, before moving higher still.
Immigration and the Workforce
This brings us to immigration. Of the 3.3 million increase in the U.S. population in the year that ended July 1st, 2024, fully 2.8 million came from net immigration, largely reflecting a surge of unauthorized immigrants over the southern border. However, the pace of this migration has fallen sharply. In the fourth quarter of 2023, U.S. Customs and Border Protection encounters with people crossing the southern border averaged 262,000 per month. By the fourth quarter of 2024, these encounters had fallen to 99,000 per month and, in January, they fell further to 61,000. Given the addition of military resources to both sides of the border and the chilling effect of the hard line taken by the president, it is quite possible that these numbers will fall further in the months ahead.
In addition to unauthorized immigrants, the U.S. issued roughly 670,000 immigration visas at foreign embassies in 2024, compared to 590,000 in 2023. However, this flow could also diminish going forward due to the president’s executive order requiring heightened vetting of noncitizens seeking entry or status and layoffs at the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services.
Finally, there are deportations. While the administration signaled an intention to focus its deportation efforts on immigrants with criminal offences, (apart from their unauthorized status), these deportations could broaden this year and gradually include a greater number of the more than 11 million unauthorized immigrants estimated to be living in the United States5. Indeed it is possible that this year or next deportations could entirely offset new immigration, resulting in close to zero net immigration for the first time since World War II.
This, of course, is highly dependent on the intensity with which the new administration pursues its policies on immigration and whether this intensity continues into the future. However, if net immigration were to approach zero, it would result in dramatically slower population growth, and slowing growth in the demand for housing and basic consumer goods and services.
Moreover, it is worth noting that, because of the age profile of the resident U.S. population and the age profile of immigrants, a zero-immigration scenario would have more dramatic impacts on the labor force than on the overall population. According to a Brookings Institute report6 76% of immigrants arriving in 2021 and 2022 were between the ages of 16 and 64, compared to roughly 64% of the already resident population. Also, while immigrants in general work across many industries, unauthorized immigrants particularly work in areas such as construction, housecleaning, restaurants, retail, home health care, childcare and landscaping. Fewer available workers in these areas could lead to higher wages for those who were available to work.
Demographics and the Investment Landscape
In a volatile economic and financial environment, forecasters often regard demographics as a given - the one variable that they put into their forecasts with a high degree of confidence. However, in 2025, American demographics are by no means “a given”. Since its inception, the United States has seen strong population growth, as a healthy excess of births over deaths has been supplemented by waves of immigration. This is why, even in recent years, the U.S. has seen population growth while the populations of countries like China, Germany, Italy, Russia and Japan have all been declining.
However, this is changing and if, after a period of very strong and chaotic unauthorized immigration, U.S. policies result in an extended period of near zero immigration, forecasters will have to mark down their estimates of population and labor force growth and increase their estimates of inflation, interest rates and capital spending on productivity-enhancing equipment. As in so many other areas, investors will have to watch Washington as much as the markets to assess how to adjust investment strategy for demographics in 2025.
