Recent data release showed marginal improvement in growth environment, which may also help to stabilize investor sentiment. However, investors may need to stay patient for clearer policy signals.
In brief
- The major Chinese economic indicators stabilized in the last months of 2023, reflecting some effects from the stimulus measures.
- Consumer sentiment, private business as well as property market confidence will likely remain subdued, requiring stronger stimulus.
- Fiscal policies supported by monetary policy tools should play the key role as a jump starter of China’s economic engine.
- Chinese stocks are trading at attractive valuations, and there are structural growth opportunities for long-term allocation. There might be further policy catalysts in upcoming months.
The major Chinese economic indicators stabilized in the last months of 2023, after sustained weakness since 2Q23. Year-over-year real GDP growth rate bottomed out in the fourth quarter, while the low base in 4Q 2022 was likely the major contributor. On a monthly basis, fixed asset investment and industrial production data revealed some positive effects from policy stimulus. That said, consumer sentiment, private business as well as property market confidence will likely remain subdued, and stronger fiscal stimulus are essential to support growth and market confidence.
Economic growth: headline readings stabilized while headwinds persist
According to the Chinese National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), China’s real GDP growth reached 5.2% year-over-year (y/y) in 4Q 2023 (3Q 2023: 4.9% y/y). This improving growth figure was partially driven by previous stimulus measures, while base effects in 4Q 2022 was likely a major contributor as well. In comparison with previous quarters, manufacturing sectors replaced services as the leading growth driver, with a stronger growth rate of 5.5% y/y in secondary industry (3Q 2023: 4.6%). Meanwhile, service sectors remained steady, delivering 5.3% y/y growth in tertiary industry (3Q 2023: 5.2%).
Similar to GDP readings, monthly economic indicators also pointed to stabilization of aggregate demand around year-end. Fixed asset investment increased by 4.1% y/y in Jan-Dec. 2023 (better than 2.9% consensus expectation and the first eleven months), mainly driven by infrastructure projects. Industrial production grew by 6.8% y/y, highlighting strong momentum in advanced manufacturing such as computer and electronics (9.6% y/y) and automobiles (20.0% y/y). These growth figures probably suggest continuous stimulus measures in previous quarters are taking some effects.
Despite the above encouraging figures, there are still headwinds for recovery. The foremost challenge is weak confidence among households and private business. According to NBS survey, consumer confidence stayed around the bottom in recent months, particularly in expectation for employment which might weigh on future consumption. In Dec. 2023, growth of retail sales dipped again to 7.4% y/y (Nov. 2023: 10.1%). Meanwhile, investment data pointed to dampened sentiment among private business, as the private fixed asset investment declined by 0.4% across the year.
Another major challenge is from the property market. As demand sank during the market downturn, inventory of residential property grew by 22.2% y/y, and development investment dropped 9.6% y/y in 2023. Such weakness also spilled over into related sectors, leading to 5.8% y/y decease in sales of durable goods including furniture, electrical appliances and decoration materials, which accounted for about 10% of total consumption.
Real estate is the major engine for credit expansion, as well as the pillar for local government financing. When activities in property market declined, balance sheet conditions of developers and local government financing vehicles (LGFVs) may keep deteriorating.
Policy response: stronger fiscal stimulus is essential
Since the Politburo meeting in late Jul. 2023, China has gradually escalated stimulus policies, including monetary easing, refinancing scheme for local government debt, issuance of special treasury, and relaxing property market controls. That said, these measures fell short of market expectation in terms of scale and pace, hence could merely prevent the economy from further sliding.
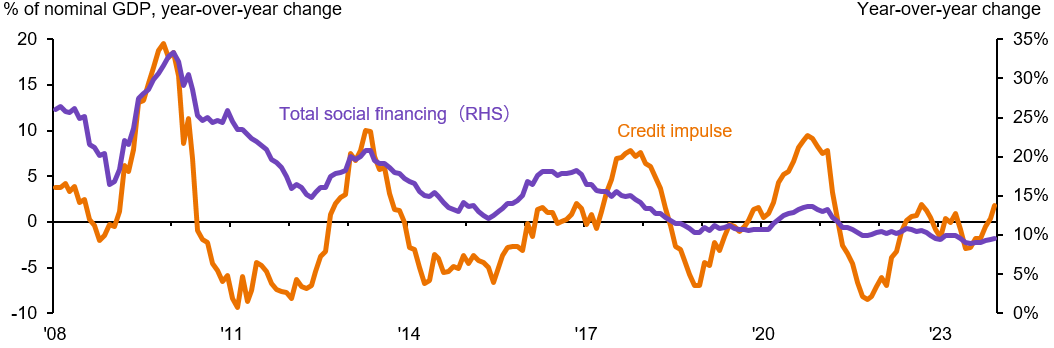
Depressed confidence has become the major obstacle hindering the effectiveness of stimulus measures. Despite continuous monetary easing and 9.7% annual growth in M2 money supply, credit impulse remained depressed as households and companies refrain from borrowing and investing (Exhibit 1), which is an exception from historical monetary easing cycles. As a result, fiscal policies should play an increasingly critical role as jump starter of the cooling economic engine.
Exhibit 1: Total social financing and credit impulse in China
Source: National Bureau of Statistics of China, People's Bank of China, J.P. Morgan Asset Management. Guide to the Markets – Asia. Data reflect most recently available as of 31/12/23.
In order to support government expenditure, the quota of government bond issuance was revised up in the second half of 2023. In August, a CNY 1.5 trillion local government refinancing bond plan was launched to support debt restructuring and refinancing by local governments in 12 provinces. In Oct. 2023, fiscal deficit ratio was lifted to 3.8% with the issuance of CNY 1 trillion special treasury bonds. It is expected that such operations will be continued, and the deficit target will once again be set at 3.8% for 2024.
To stabilize property market, it is also important to introduce incremental demands via fiscal spending. People's Bank of China relaunched its Pledged Supplementary Lending (PSL) scheme in Dec. 2023, providing CNY 350 billion via policy banks to support urban redevelopment projects by local governments. Such operation may continue in 2024 at larger scale, but the actual impact remains uncertain.
Investment implications: stay patient for policy catalyst
Recent data release showed marginal improvement in growth environment, which may also help to stabilize investor sentiment. However, investors may need to stay patient for clearer policy signals. The annual session of National People's Congress to be started on March 5 may give more details about stimulus policies and become catalyst in stock market.
The economic releases continue to suggest investment opportunities within Chinese equity market. After market correction in the past two years, valuations of Chinese stocks have already become attractive in both onshore and offshore markets. This points to upside potential when stronger stimulus measures are realized.
Meanwhile, corporate earnings will likely improve further. Based on consensus forecast, earnings per share for MSCI China are expected to grow by 15% in 2024 at forward PE of 9.3 times. On a longer horizon, emerging sectors, such as renewable energy, electric vehicles and advanced manufacturing, may serve as China’s new growth engine and are set to continue to benefit from ample policy support.