Topics: Equity markets, inflation and the Federal Reserve; what it would take for the energy bill’s projected GHG reductions to actually occur, and why it matters; and what will all those new IRS agents be doing?
Earlier in the summer, I wrote that while there might be a “hurricane” coming for the US economy, a lot of hurricanes had already taken place in equity markets:
By May, 50% of NASDAQ stocks were down by 45%, and 33% were down by 70% (May 17 EoTM), and by June the average Russell 1000 Growth and Small Cap stock was down by 50% (June 7 EoTM)
In 6 prior major recessions, equities bottomed way before GDP and by the time GDP was rising again, equities had already risen substantially (June 7 EoTM)
Investor capitulation: an all-time high on the % of stocks trading below their cash value (June 27 EoTM)
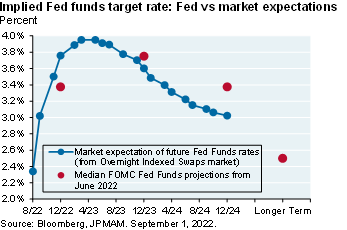
As a result, I was not surprised to see markets bounce from their June lows, particularly as hedge funds covered short positions1. That said, I was surprised at the breadth of the rally since the terminal Fed Funds rate for this cycle is still unknown. We may be past peak consumer price inflation, but the Funds rate required to bring inflation down to the Fed’s target2, and its impact on corporate earnings, is still unknown.
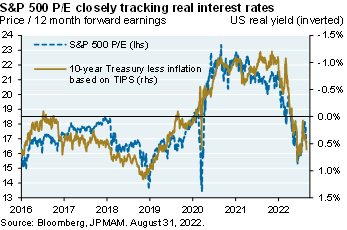
Markets and multiples. Markets are pricing a Fed Funds peak of 4% by April, followed by a decline to 3% by year-end 2024. While inflation linked to food/energy, auto parts, other goods and cyclical services are rolling over, less cyclical services and housing inflation are still rising [Ex. 1 and 2; see p.7-8]. And while business surveys suggest that wage pressures have subsided from peak levels, wage growth is still extremely high [Ex. 3 and 4] and payrolls and jobless claims have only weakened a small amount. If the Fed is committed to restoring positive real interest rates (see chart, right), I find it hard to justify an increase in equity multiples.
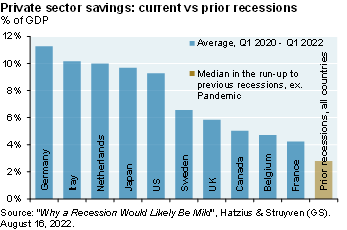
The recent equity rally is often compared to two prior bear market rallies, but both involved deep recessions (1973-1975 and 2007-2009) that we do not anticipate this time. To be clear, a recession is still a significant risk over the next few months. The US avoided recession four times after prior Fed hiking cycles but each time, food/energy inflation was very low which isn’t the case today [Ex. 5]. Furthermore, new orders have declined sharply relative to production, inventories are high [Ex. 6 and 7], housing is imploding and the US dollar is at a 20-year high (hurting 30%-40% of S&P revenues which are foreign-sourced). If there is a recession, I expect it to be a milder one: private sector savings are higher than before prior recessions, and a macroeconomic projection of the US business cycle points to a less severe contraction than in 2009 or 2020.
Bottom line for equity investors:
While consumer price inflation may have seen its peak, it’s still elevated and wage inflation has not rolled over yet [Ex. 4]. The labor force participation rate is still below pre-COVID levels [Ex. 8], but since almost all of the gap is due to the age 54+ cohort, there’s less room for continued improvement (the LFPR for ages 25-54 is now back at pre-COVID levels). Furthermore, a measure of jobs openings plus employment vs the labor force shows the tightest labor markets in decades. So, the Fed will keep tightening. But if there is a recession, we expect it to be a milder one given the health of consumer balance sheets
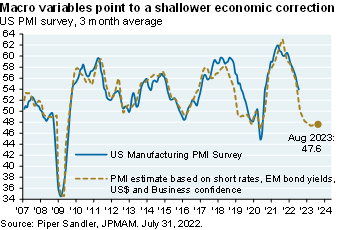
Leading indicators for the PMI manufacturing survey point to a mild recession next year (see chart above). The declining PMI is also a key input into leading indicators for S&P earnings [Ex.9]. The summer rally was due to rising P/E multiples [Ex. 10] which are unlikely to rise further given positive real interest rates and more quantitative tightening. Given weakening leading indicators and declining earnings, I expect a rollover in US equity markets this fall closer to the June lows for those looking for a better entry point
The last Fed hike for the cycle, when it does occur, has historically been good news for investors; only during the 2000 cycle did the last Fed hike fail to result in a sustained rally [Ex. 11]
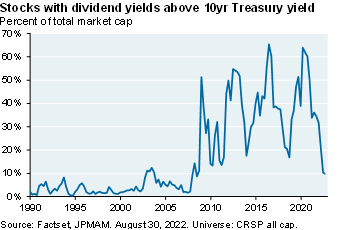
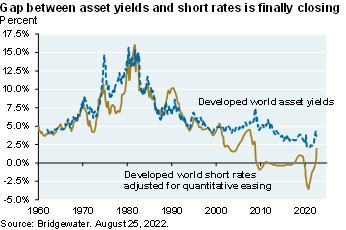
See the two charts below: since 2009, financial repression resulted in 20%-60% of the stock market offering dividend yields above Treasury yields, and resulted in short rates that were way below asset yields. Both trends were only sustainable if inflation stayed low forever. Some of you will miss TINA investing (e.g., “There Is No Alternative” to equities since interest rates are below inflation). I won’t. It spawned a lot of mindless risk-taking and ruined fixed income markets for a generation, negatively impacting defined benefit plans, insurers and families invested in funds that reduce risk with age. Good riddance to bad policy
What it would take for the energy bill’s projected GHG reductions to actually occur, and why it matters
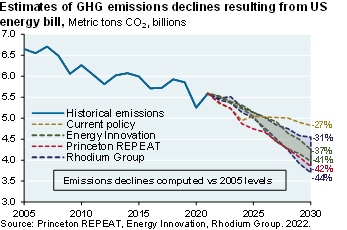
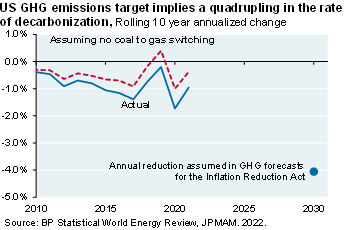
I read a piece in the Atlantic entitled “The Best Evidence Yet That the Climate Bill Will Work” [August 3, 2022]. The author writes: “First we got the bill. Now we have the numbers”. Really? What you have are projections from three energy modeling teams estimating that the bill could reduce GHG emissions by ~40% by 2030 vs 2005 levels, implying a quadrupling in the pace of decarbonization. There’s no discussion in the Atlantic article of what would actually have to happen to get there.
I looked at the detailed assumptions made by one of the modeling teams. These analysts are very smart and very well informed on energy transition dynamics. But: their models often assume perfectly optimal behavior by businesses and individuals based on prevailing incentives, and usually ignore frictional issues such as battery and critical mineral supply chain constraints3, interconnection delays of wind/solar power and the difficulty in siting new transmission. On the latter, House Democrats may block passage of the infrastructure project siting bill that Senate Democrats agreed to in exchange for Manchin’s Inflation Reduction Act support4.
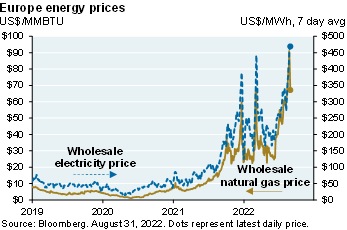
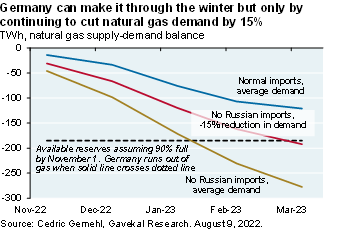
The next page compares their assumptions and ours. The reason this is important: if you believe the energy bill modelers, the US could start enacting policies to constrain the natural gas industry since the US will need a lot less gas in 2030, and even less after that. But if you believe that the future could be closer to our assumptions, you would do no such thing for fear of ending up like Europe: energy-dependent and facing a difficult winter. With gas reserves headed for 90% by November it looks like Germany will be able to make it through the winter without Russian gas, but only if they continue to cut consumption by 15% vs normal levels.
Understanding the table. The table compares our assumptions for the year 2030 with one of the three modeling groups that analyzed the energy bill on behalf of the Senate. The color-coded column highlights the greatest differences between our assumptions and theirs; red = very different, green = very similar, white = neutral, yellow = small different.
I emphasized the natural gas share of primary energy since it is a critical policy issue. It affects decisions on pipelines, electricity transmission, energy storage, export policy (European demand for LNG is expected to rise by 2.5x by 2030), winter heating regulations and decommissioning policies affecting coal/nuclear.
| 2021 | Assumption | JPM 2030 | Group X 2030 | Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy consumption | |||||
| Final energy delivered, growth vs 2021 | 0% | -2% | Many forecasts of US energy demand are roughly flat, reflecting increased efficiency and reduced energy intensity offsetting population growth | ||
| Electricity consumption growth vs 2021 | 4% | 25% | |||
| 20% | Electrification of final energy delivered | 21% | 26% | ||
| 17% | Electrification of industrial energy use | 17% | 18% | ||
| Fossil Fuels | Primary energy figures based on EIA/BP convention of grossing up renewable energy generation by a 35% thermal equivalent | ||||
| 34% | Natural gas share of primary energy consumption | 32% | 20% | Excludes any US natural gas produced and exported for economic/NATO reasons | |
| 39% | Natural gas share of electricity consumption | 31% | 15% | ||
| 10% | Coal share of primary energy consumption | 4% | 5% | Despite potential for CCS to extend life of coal plants, shares of generation/primary energy still projected to decline | |
| NA | Decline in gasoline/diesel consumption vs 2021 level | -10% | -28% | ||
| 6% | Biodiesel and renewable diesel share of diesel production | 8% | ?? | Renewable fuel credit only extended to 2024 |
Source: Modeling Group X, EIA, BP, JPMAM. 2022.
| 2021 | Assumption | JPM 2030 | Group X 2030 | Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wind and solar | |||||
| 109 | Solar plus wind watts per capita per year of new capacity, 2022-2030 annual average | 162 | 302 | The largest amount of annual new electricity generation capacity ever installed in the US was 197 watts per capita, achieved in 2002 due to a surge in natural gas capacity | |
| Solar capacity additions (annual) 2022-2030 vs 2019-2021 pace | 3.4x | 6.9x | |||
| 4% | Solar share of electricity generation | 18% | 30% | ||
| 25% | Solar capacity factor | 25% | 25% | ||
| Wind capacity additions (annual) 2022-2030 vs 2019-2021 pace | 1.7x | 2.7x | |||
| 9% | Wind share of electricity generation | 22% | 28% | ||
| 35% | Wind capacity factor | 35% | 35% | ||
| Electric vehicles | EV category includes battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug in hybrids (PHEVs), excludes hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). Any forecast must incorporate domestic/allied sourcing requirements for critical minerals and batteries included in the energy bill for $7500 subsidies to be available | ||||
| 4% | Passenger car/light truck/SUV EV share of sales in 2030 | 25%-40% | 100% | ||
| 1% | Passenger car/light truck/SUV EV share of fleet in 2030 | 10%-15% | 23% | ||
| 2.8 | Passenger car/light truck/SUV EV miles per kWh in 2030 | 3.3 | 3.3 | ||
| 0% | Medium duty truck EV share of sales in 2030 | 28% | 88% | ||
| 0% | Medium duty truck EV share of fleet in 2030 | 10% | 33% | ||
| 1.7 | Medium duty truck EV miles per kWh in 2030 | 1.9 | 1.9 | ||
| 0% | Heavy duty truck EV share of sales in 2030 | 28% | 92% | ||
| 0% | Heavy duty truck EV share of fleet in 2030 | 10% | 28% | ||
| 0.5 | Heavy duty truck EV miles per kWh in 2030 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
Source: Modeling Group X, EIA, BP, JPMAM. 2022.
| 2021 | Assumption | JPM 2030 | Group X 2030 | Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Other assumptions | |||||
| 22.9 | Passenger car/light truck/SUV ICE car miles per gallon | 27.5 | 29.5 | ||
| 19% | Nuclear share of electricity consumption | 15% | 17% | Many unprofitable nuclear plants assumed to remain open due to IRA production tax credits | |
| 5%-10% | Cumulative transmission grid growth, 2021-2030 | 10% | 37% | The historical 2021 figure of 10% represents the trailing 10 year grid expansion level, measured in GW-miles. Highly dependent on changes in Federal/state siting policies and eminent domain | |
| 6% | Electric heat pump share of residential and commercial heating | 22% | 21% | Significant grid implications depending on whether backup thermal heating systems remain, or if generation/distribution systems will have to handle coldest days of the year when electricity demand surges | |
| 0.8% | Hydrogen share of final energy consumption | 1.0% | 1.5% | Hydrogen is an energy carrier, not an energy source; projected increases vs 2021 are assumed to be from green hydrogen (renewable electrolysis), blue hydrogen (steam reformation of natural gas + CCS) or turquoise hydrogen (gasification or pyrolysis of MSW) | |
| 27.1 | Electricity stored and consumed later via pumped storage and other utility scale storage (batteries, flywheels, etc), TWh | 136.9 | 46.3 | Energy storage can reduce the need for gas peaker plants, transmission investment and smooth intraday demand imbalances | |
| 21 | US carbon sequestration, million metric tons per year | 150 | 200 | While 45Q tax credits have catalyzed greater industrial interest in CCS, as of 2021, less than 1% of US CO2 was geologically sequestered. A forecast of 200 MMT per year would represent 10x growth but still represent just 3%-5% of current and future US CO2 emissions |
Source: Modeling Group X, EIA, BP, JPMAM. 2022.
What will all those new IRS agents be doing?
The Inflation Reduction Act will dedicate $45 billion for tens of thousands of new IRS agents focused on tax enforcement, which the CBO estimates will raise $203 billion in additional revenues over a ten year period for a ~4x return. Sounds easy, doesn’t it? Not so fast; a May 2022 report from the General Accounting Office suggests this could be difficult to do, particularly if the IRS directs new agents to only audit taxpayers with more than $400k in income as requested by Treasury Secretary Yellen and as reiterated by IRS Commissioner Rettig.
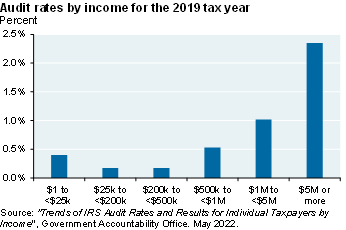
The audit rate of individual income tax returns fell from 0.90% in 2010 to 0.25% in 2019. This decline is mostly attributed to reduced IRS funding and attrition of IRS agents. Audit rates decreased the most for those with incomes over $200k, although audits are still skewed towards incomes of $1mm+ (chart, left)
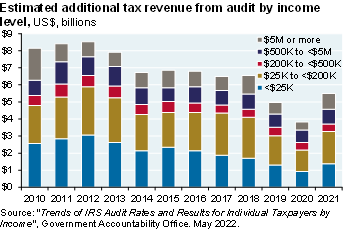
From 2010 to 2019, incremental taxes raised were highest for audits of those earning less than $200k (chart, right); the average percent change in the amount owed was highest for this category as well
In contrast, higher incomes had the highest rate of “no change to taxes owed” after audit
Let’s assume that the audit rate for those earning more than $400k reverts back to 2010 levels (i.e., it increases by a factor of 7x). We estimate that this would raise $8-$10 billion per year in 2031 based on data in the GAO report, far short of the $35 billion estimated by the CBO
So, I’m not sure how the Act will raise the assumed revenues if new agents only focus on wealthier taxpayers. In late August, the CBO sent a letter to the House Ways and Means Committee indicating that they had already cut their estimate of revenues raised from $203 billion to $180 billion.
Also: is the tax gap as large as advertised? What may be driving this initiative are estimates of a $300-$600 billion “tax gap” per year according to the Treasury5: the difference between what should be paid and what is paid. Most of the gap is due to underreporting of income rather than non-payment or non-filing. However, analysts at the Brookings Tax Policy Center cite several issues that result in tax gap overestimation 6:
The tax gap cited above includes additional taxes recommended by examiners even if the amount could be reversed on appeal or court challenge. And such reversals can be large: only 63% of additional taxes recommended from 2015 through 2019 were ultimately assessed after administrative appeals and abatements. That figure is likely to be even lower after further reductions following judicial review
The IRS uses “detection controlled estimations” in its compliance studies to scale up the recommendations of all examiners to match those with the largest upward adjustments in personal income. In other words, the process is leveraged to revisions made by examiners with the largest estimates of income under-reporting. This “highest common denominator” approach is estimated to account for two thirds (!!) of the entire individual income tax underreporting gap
The Treasury’s estimate of the tax gap is partially based on a 2007 study citing $1 trillion in US taxpayer offshore wealth and non-payment of taxes on offshore interest and dividends. However: the IRS ramped up offshore enforcement efforts in 2008 after financial institutions in Switzerland, Liechtenstein, Israel and the Caribbean turned over thousands of names to the IRS, resulting in $6 billion in penalties paid. Since then, another $11 billion in penalties were paid by 56,000 taxpayers entering into the IRS Offshore Voluntary Disclosure Program. The Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act of 2010 made it even harder for US taxpayers to hide assets, and the IRS/Justice Department have consistently prosecuted FBAR violations over last decade, penalizing financial institutions that harbor violators. Bottom line: a lot has changed since 2007
The Tax Cut and Jobs Act of 2017 caused more taxpayers to claim standard rather than itemized deductions, and the C Corporation tax rate declined from 35% to 21%; both are likely to reduce the degree of underreporting of income
Some components of the tax gap reflect taxpayer-IRS disputes regarding the timing of depreciation deductions. While their resolution could increase taxes due in a given year, they do not imply perpetual underreporting of income since taxes due in future years would be lower in these cases
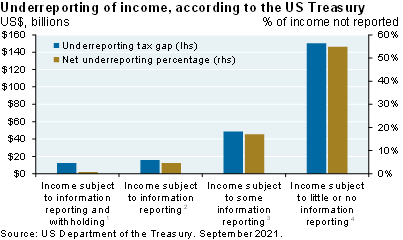
Whatever the tax gap is, new IRS agents are likely to focus on partnerships, sole proprietorships and owners of commercial and residential rental properties7. The Treasury believes that income underreporting could be 50%-60% for these entities given less withholding and information reporting (see chart). The Brookings paper also cites underreporting of pass-through income as a factor resulting in tax gap underestimation.
Last point: if you hold a lot of crypto, they may be coming for you as well if you exchange crypto for goods and services without recognizing appreciation as capital gains8.
1. Includes wages and salaries
2. Includes pensions, annuities, unemployment compensation, dividend income, interest income and taxable Social Security benefits
3. Includes partnership/S corporation income, capital gains and alimony income
4. Includes nonfarm proprietor income, other income, rents and royalties, farm income and Form 4797 income
Exhibits
Exhibit 1: inflation trends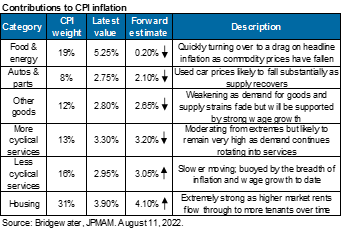
Exhibit 2: housing inflation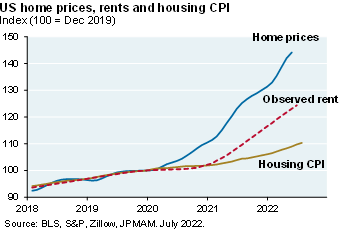
Exhibit 3: wage expectations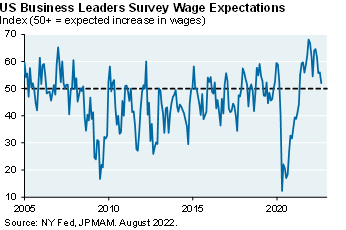
Exhibit 4: consumer price and wage inflation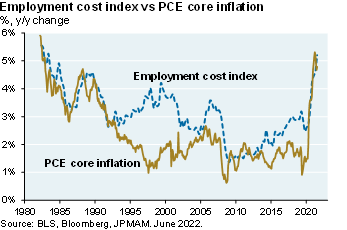
Exhibit 5: the only time the US has avoided recession when the Fed hikes is when food/energy inflation is low (as shown in the red bars)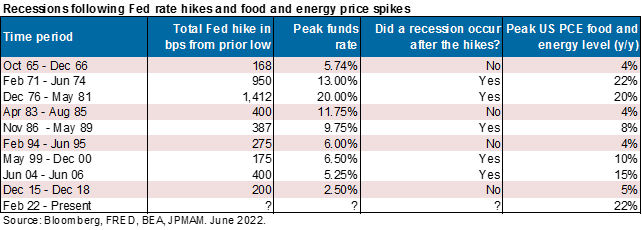
Exhibit 6: leading indicators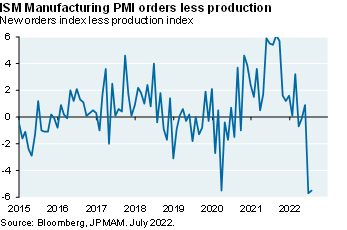
Exhibit 7: inventories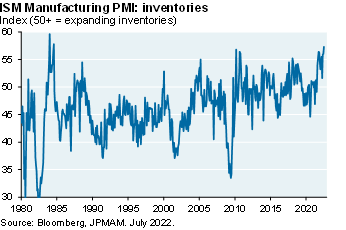
Exhibit 8: labor force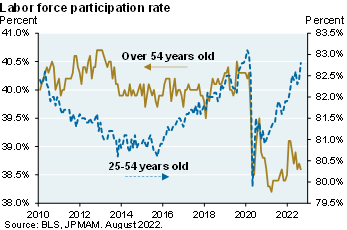
Exhibit 9: leading indicator for earnings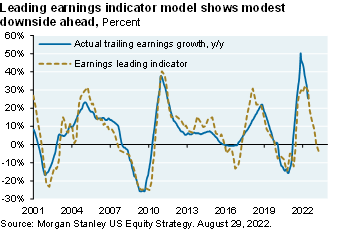
Exhibit 10: price-to-earnings ratios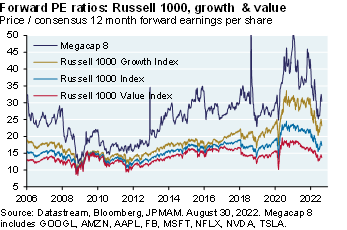
Exhibit 11: equities and the last Fed hike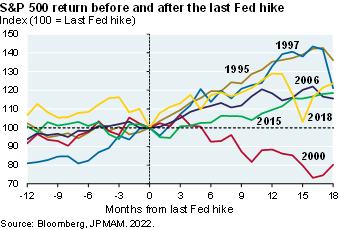
2 Rob Portman (R-OH), a Senator I admire greatly and whose retirement is another sign of institutional decay in the Senate, released a report this year on how China's government targeted Federal Reserve employees in a decade-long infiltration campaign aimed at stealing US monetary policy secrets. My question: wouldn’t the Fed’s very poor track record in anticipating future inflation and policy rates dissuade people from wanting to steal its secrets and copy it?
3 Domestic content requirements for EV subsidies in the energy bill. Critical mineral minimum extraction/processing percentages for US/Free Trade Area countries start at 40% in 2024 and rise to 80% by 2027. Battery component requirements for manufacturing or assembly in North America start at 50% in 2024 and also rise to 80% by 2027.
4 “Prospects dim in House for Manchin’s federal permitting measure”, Rollcall.com, August 17, 2022
5 “The Case for a Robust Attack on the Tax Gap”, US Treasury, September 7, 2021
6 “The Tax Gap’s Many Shades of Gray”, Hemel, Holtzblatt and Rosenthal (TPC), September 30, 2021
7 A partial list of what the IRS looks for: allocations of ordinary income to tax-exempt partners, and allocations of deductions/long term gains to partners in high tax brackets, that are not in accordance with ownership interests; S corporations that do not pay sufficient wages to shareholder-employees, or which provide them with large non-wage distributions; work arrangements improperly structured as independent contractors so as to benefit from expanded pretax deferral options and qualified business income deductions.
8 The IRS reportedly believes that there is a large degree of non-reporting by crypto holders. Recent new rules include Executive Order 14067 instructing the IRS to focus on non-compliance; enhanced Form 1040 disclosure on crypto sales, exchanges and receipts; and Notice 2014-21/Rev. Rule 2019-24 providing guidance on crypto tax treatment. What may come next: comprehensive field exams of digital asset funds, principals and investors; enhanced information disclosures piercing some bearer aspects of crypto holdings; and assessment of economic and possibly criminal penalties which are well publicized in order to raise the bar for non-compliance.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
This report uses rigorous security protocols for selected data sourced from Chase credit and debit card transactions to ensure all information is kept confidential and secure. All selected data is highly aggregated and all unique identifiable information, including names, account numbers, addresses, dates of birth, and Social Security Numbers, is removed from the data before the report’s author receives it. The data in this report is not representative of Chase’s overall credit and debit cardholder population.
The views, opinions and estimates expressed herein constitute Michael Cembalest’s judgment based on current market conditions and are subject to change without notice. Information herein may differ from those expressed by other areas of J.P. Morgan. This information in no way constitutes J.P. Morgan Research and should not be treated as such.
The views contained herein are not to be taken as advice or a recommendation to buy or sell any investment in any jurisdiction, nor is it a commitment from J.P. Morgan or any of its subsidiaries to participate in any of the transactions mentioned herein. Any forecasts, figures, opinions or investment techniques and strategies set out are for information purposes only, based on certain assumptions and current market conditions and are subject to change without prior notice. All information presented herein is considered to be accurate at the time of production. This material does not contain sufficient information to support an investment decision and it should not be relied upon by you in evaluating the merits of investing in any securities or products. In addition, users should make an independent assessment of the legal, regulatory, tax, credit and accounting implications and determine, together with their own professional advisers, if any investment mentioned herein is believed to be suitable to their personal goals. Investors should ensure that they obtain all available relevant information before making any investment. It should be noted that investment involves risks, the value of investments and the income from them may fluctuate in accordance with market conditions and taxation agreements and investors may not get back the full amount invested. Both past performance and yields are not reliable indicators of current and future results.
Non-affiliated entities mentioned are for informational purposes only and should not be construed as an endorsement or sponsorship of J.P. Morgan Chase & Co. or its affiliates.
For J.P. Morgan Asset Management Clients:
J.P. Morgan Asset Management is the brand for the asset management business of JPMorgan Chase & Co. and its affiliates worldwide.
To the extent permitted by applicable law, we may record telephone calls and monitor electronic communications to comply with our legal and regulatory obligations and internal policies. Personal data will be collected, stored and processed by J.P. Morgan Asset Management in accordance with our privacy policies at https://am.jpmorgan.com/global/privacy.
ACCESSIBILITY
For U.S. only: If you are a person with a disability and need additional support in viewing the material, please call us at 1-800-343-1113 for assistance.
This communication is issued by the following entities:
In the United States, by J.P. Morgan Investment Management Inc. or J.P. Morgan Alternative Asset Management, Inc., both regulated by the Securities and Exchange Commission; in Latin America, for intended recipients’ use only, by local J.P. Morgan entities, as the case may be.; in Canada, for institutional clients’ use only, by JPMorgan Asset Management (Canada) Inc., which is a registered Portfolio Manager and Exempt Market Dealer in all Canadian provinces and territories except the Yukon and is also registered as an Investment Fund Manager in British Columbia, Ontario, Quebec and Newfoundland and Labrador. In the United Kingdom, by JPMorgan Asset Management (UK) Limited, which is authorized and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority; in other European jurisdictions, by JPMorgan Asset Management (Europe) S.à r.l. In Asia Pacific (“APAC”), by the following issuing entities and in the respective jurisdictions in which they are primarily regulated: JPMorgan Asset Management (Asia Pacific) Limited, or JPMorgan Funds (Asia) Limited, or JPMorgan Asset Management Real Assets (Asia) Limited, each of which is regulated by the Securities and Futures Commission of Hong Kong; JPMorgan Asset Management (Singapore) Limited (Co. Reg. No. 197601586K), which this advertisement or publication has not been reviewed by the Monetary Authority of Singapore; JPMorgan Asset Management (Taiwan) Limited; JPMorgan Asset Management (Japan) Limited, which is a member of the Investment Trusts Association, Japan, the Japan Investment Advisers Association, Type II Financial Instruments Firms Association and the Japan Securities Dealers Association and is regulated by the Financial Services Agency (registration number “Kanto Local Finance Bureau (Financial Instruments Firm) No. 330”); in Australia, to wholesale clients only as defined in section 761A and 761G of the Corporations Act 2001 (Commonwealth), by JPMorgan Asset Management (Australia) Limited (ABN 55143832080) (AFSL 376919). For all other markets in APAC, to intended recipients only.
For J.P. Morgan Private Bank Clients:
ACCESSIBILITY
J.P. Morgan is committed to making our products and services accessible to meet the financial services needs of all our clients. Please direct any accessibility issues to the Private Bank Client Service Center at 1-866-265-1727.
LEGAL ENTITY, BRAND & REGULATORY INFORMATION
In the United States, bank deposit accounts and related services, such as checking, savings and bank lending, are offered by JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. Member FDIC.
JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. and its affiliates (collectively “JPMCB”) offer investment products, which may include bank-managed investment accounts and custody, as part of its trust and fiduciary services. Other investment products and services, such as brokerage and advisory accounts, are offered through J.P. Morgan Securities LLC (“JPMS”), a member of FINRA and SIPC. Annuities are made available through Chase Insurance Agency, Inc. (CIA), a licensed insurance agency, doing business as Chase Insurance Agency Services, Inc. in Florida. JPMCB, JPMS and CIA are affiliated companies under the common control of JPM. Products not available in all states.
In Germany, this material is issued by J.P. Morgan SE, with its registered office at Taunustor 1 (TaunusTurm), 60310 Frankfurt am Main, Germany, authorized by the Bundesanstalt für Finanzdienstleistungsaufsicht (BaFin) and jointly supervised by the BaFin, the German Central Bank (Deutsche Bundesbank) and the European Central Bank (ECB). In Luxembourg, this material is issued by J.P. Morgan SE – Luxembourg Branch, with registered office at European Bank and Business Centre, 6 route de Treves, L-2633, Senningerberg, Luxembourg, authorized by the Bundesanstalt für Finanzdienstleistungsaufsicht (BaFin) and jointly supervised by the BaFin, the German Central Bank (Deutsche Bundesbank) and the European Central Bank (ECB); J.P. Morgan SE – Luxembourg Branch is also supervised by the Commission de Surveillance du Secteur Financier (CSSF); registered under R.C.S Luxembourg B255938. In the United Kingdom, this material is issued by J.P. Morgan SE – London Branch, registered office at 25 Bank Street, Canary Wharf, London E14 5JP, authorized by the Bundesanstalt für Finanzdienstleistungsaufsicht (BaFin) and jointly supervised by the BaFin, the German Central Bank (Deutsche Bundesbank) and the European Central Bank (ECB); J.P. Morgan SE – London Branch is also supervised by the Financial Conduct Authority and Prudential Regulation Authority. In Spain, this material is distributed by J.P. Morgan SE, Sucursal en España, with registered office at Paseo de la Castellana, 31, 28046 Madrid, Spain, authorized by the Bundesanstalt für Finanzdienstleistungsaufsicht (BaFin) and jointly supervised by the BaFin, the German Central Bank (Deutsche Bundesbank) and the European Central Bank (ECB); J.P. Morgan SE, Sucursal en España is also supervised by the Spanish Securities Market Commission (CNMV); registered with Bank of Spain as a branch of J.P. Morgan SE under code 1567. In Italy, this material is distributed by J.P. Morgan SE – Milan Branch, with its registered office at Via Cordusio, n.3, Milan 20123, Italy, authorized by the Bundesanstalt für Finanzdienstleistungsaufsicht (BaFin) and jointly supervised by the BaFin, the German Central Bank (Deutsche Bundesbank) and the European Central Bank (ECB); J.P. Morgan SE – Milan Branch is also supervised by Bank of Italy and the Commissione Nazionale per le Società e la Borsa (CONSOB); registered with Bank of Italy as a branch of J.P. Morgan SE under code 8076; Milan Chamber of Commerce Registered Number: REA MI 2536325. In the Netherlands, this material is distributed by J.P. Morgan SE – Amsterdam Branch, with registered office at World Trade Centre, Tower B, Strawinskylaan 1135, 1077 XX, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, authorized by the Bundesanstalt für Finanzdienstleistungsaufsicht (BaFin) and jointly supervised by the BaFin, the German Central Bank (Deutsche Bundesbank) and the European Central Bank (ECB); J.P. Morgan SE – Amsterdam Branch is also supervised by De Nederlandsche Bank (DNB) and the Autoriteit Financiële Markten (AFM) in the Netherlands. Registered with the Kamer van Koophandel as a branch of J.P. Morgan SE under registration number 72610220. In Denmark, this material is distributed by J.P. Morgan SE – Copenhagen Branch, filial af J.P. Morgan SE, Tyskland, with registered office at Kalvebod Brygge 39-41, 1560 København V, Denmark, authorized by the Bundesanstalt für Finanzdienstleistungsaufsicht (BaFin) and jointly supervised by the BaFin, the German Central Bank (Deutsche Bundesbank) and the European Central Bank (ECB); J.P. Morgan SE – Copenhagen Branch, filial af J.P. Morgan SE, Tyskland is also supervised by Finanstilsynet (Danish FSA) and is registered with Finanstilsynet as a branch of J.P. Morgan SE under code 29010. In Sweden, this material is distributed by J.P. Morgan SE – Stockholm Bankfilial, with registered office at Hamngatan 15, Stockholm, 11147, Sweden, authorized by the Bundesanstalt für Finanzdienstleistungsaufsicht (BaFin) and jointly supervised by the BaFin, the German Central Bank (Deutsche Bundesbank) and the European Central Bank (ECB); J.P. Morgan SE – Stockholm Bankfilial is also supervised by Finansinspektionen (Swedish FSA); registered with Finansinspektionen as a branch of J.P. Morgan SE. In France, this material is distributed by JPMCB, Paris branch, which is regulated by the French banking authorities Autorité de Contrôle Prudentiel et de Résolution and Autorité des Marchés Financiers. In Switzerland, this material is distributed by J.P. Morgan (Suisse) SA, with registered address at rue de la Confédération, 8, 1211, Geneva, Switzerland, which is authorised and supervised by the Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA), as a bank and a securities dealer in Switzerland. Please consult the following link to obtain information regarding J.P. Morgan’s EMEA data protection policy: https://www.jpmorgan.com/privacy.
In Hong Kong, this material is distributed by JPMCB, Hong Kong branch. JPMCB, Hong Kong branch is regulated by the Hong Kong Monetary Authority and the Securities and Futures Commission of Hong Kong. In Hong Kong, we will cease to use your personal data for our marketing purposes without charge if you so request. In Singapore, this material is distributed by JPMCB, Singapore branch. JPMCB, Singapore branch is regulated by the Monetary Authority of Singapore. Dealing and advisory services and discretionary investment management services are provided to you by JPMCB, Hong Kong/Singapore branch (as notified to you). Banking and custody services are provided to you by JPMCB Singapore Branch. The contents of this document have not been reviewed by any regulatory authority in Hong Kong, Singapore or any other jurisdictions. You are advised to exercise caution in relation to this document. If you are in any doubt about any of the contents of this document, you should obtain independent professional advice. For materials which constitute product advertisement under the Securities and Futures Act and the Financial Advisers Act, this advertisement has not been reviewed by the Monetary Authority of Singapore. JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. is a national banking association chartered under the laws of the United States, and as a body corporate, its shareholder’s liability is limited.
With respect to countries in Latin America, the distribution of this material may be restricted in certain jurisdictions. We may offer and/or sell to you securities or other financial instruments which may not be registered under, and are not the subject of a public offering under, the securities or other financial regulatory laws of your home country. Such securities or instruments are offered and/or sold to you on a private basis only. Any communication by us to you regarding such securities or instruments, including without limitation the delivery of a prospectus, term sheet or other offering document, is not intended by us as an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any securities or instruments in any jurisdiction in which such an offer or a solicitation is unlawful. Furthermore, such securities or instruments may be subject to certain regulatory and/or contractual restrictions on subsequent transfer by you, and you are solely responsible for ascertaining and complying with such restrictions. To the extent this content makes reference to a fund, the Fund may not be publicly offered in any Latin American country, without previous registration of such fund’s securities in compliance with the laws of the corresponding jurisdiction. Public offering of any security, including the shares of the Fund, without previous registration at Brazilian Securities and Exchange Commission— CVM is completely prohibited. Some products or services contained in the materials might not be currently provided by the Brazilian and Mexican platforms.
JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. (JPMCBNA) (ABN 43 074 112 011/AFS Licence No: 238367) is regulated by the Australian Securities and Investment Commission and the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority. Material provided by JPMCBNA in Australia is to “wholesale clients” only. For the purposes of this paragraph the term “wholesale client” has the meaning given in section 761G of the Corporations Act 2001 (Cth). Please inform us if you are not a Wholesale Client now or if you cease to be a Wholesale Client at any time in the future.
JPMS is a registered foreign company (overseas) (ARBN 109293610) incorporated in Delaware, U.S.A. Under Australian financial services licensing requirements, carrying on a financial services business in Australia requires a financial service provider, such as J.P. Morgan Securities LLC (JPMS), to hold an Australian Financial Services Licence (AFSL), unless an exemption applies. JPMS is exempt from the requirement to hold an AFSL under the Corporations Act 2001 (Cth) (Act) in respect of financial services it provides to you, and is regulated by the SEC, FINRA and CFTC under U.S. laws, which differ from Australian laws. Material provided by JPMS in Australia is to “wholesale clients” only. The information provided in this material is not intended to be, and must not be, distributed or passed on, directly or indirectly, to any other class of persons in Australia. For the purposes of this paragraph the term “wholesale client” has the meaning given in section 761G of the Act. Please inform us immediately if you are not a Wholesale Client now or if you cease to be a Wholesale Client at any time in the future.
This material has not been prepared specifically for Australian investors. It:
May contain references to dollar amounts which are not Australian dollars;
May contain financial information which is not prepared in accordance with Australian law or practices;
May not address risks associated with investment in foreign currency denominated investments; and
Does not address Australian tax issues.
On CPI, S&P, GHG and the IRS
Three topics in this month’s Eye on the Market. First, an update on the Fed, inflation and corporate profits since we believe the June equity market lows may be retested in the fall.
[START RECORDING]
FEMALE VOICE 1: --podcast has been prepared exclusively for institutional wholesale professional clients and qualified investors only, as defined by local laws and regulations. Please read other important information which can be found in the link at the end of the podcast episode.
MR. MICHAEL CEMBALEST: Good afternoon, and welcome to the Labor Day "Eye on the Market" podcast. I haven't recorded something in awhile, so welcome back to everybody who listens to this podcast, and I hope you had a nice end to your summer.
So, there are three sections in the market this month. A general discussion of what's going on in equity markets, inflation, and the federal reserve, what it would take for the energy bill's projected GHG reductions to actually occur, and why I think that matters so much, and then lastly a look at what all those new IRS agents might be doing, because that was another big part of the inflation reduction act.
To get started, let's talk about what's going on in the markets. Earlier in the summer I wrote that while there might be a hurricane coming for the U.S. economy, a lot of the damage had already been done in the equity markets, and in May and June we showed all sorts of these charts on how the average NASDAQ stock was down 45%; a third of them were down 70%. How in prior recessions the equities bottom way before GDP and earnings, and by the time GDP and earnings are rising again, equities have already rallied a lot. We looked at some measure of investor capitulation that were pretty compelling.
So, I wasn't surprised to see a bounce from the June lows, and particularly since there was a lot of hedge funds that had some short positions they had to cover. That said, I was a little surprised at the breadth of the rally, because we really don't know where the terminal funds rate is going, and all it took was a tiny little speech from Powell after Jackson Hole to kind of usher in another little mini correction here.
So, here's where things stand right now. The markets are pricing in a peak fed funds rate of around 3.9% by next April, followed by a decline to 2.9% by the end of 2024. In other words, funds are at peaks next April and then gradually start declining. I don't know about that. Inflation that's linked to food and energy and auto parts and used cards and certain things, they're starting to roll over.
The less-cyclical service and housing inflation numbers are still rising, and some of the business survey suggests that the wage pressures have peaked, but the actual wage growth numbers are still really high and unrelentingly rising. Then payrolls and jobless claims have only weakened a small amount. As a result, what you get is the equity markets trading almost lockstep with the tenure treasury less anticipated inflation, in other words, every time you get an increase in anticipated inflation, and in increase in the real rates, equity multiples go down, and then the reverse is true as well.
There's a chart here showing this, and the reason it's so important is those wacky forward earnings multiples of 20 to 22 that we had from the beginning of COVID until a few months ago was taking place because real 10-year yields were negative. So, as long as you believe that real interest rates are positive now and going to stay positive, I find it hard to justify an increase in PE multiples.
Bottom line is consumer price inflation may have seen its peak but it's still elevated. Wage inflation hasn't rolled over. The labor force participation rate has stalled which is adding to tight labor market conditions. So, I still think there's a one-in-two chance that we have a recession next year. That said, I think it's a mild one. Consumer balance sheets are much stronger than they were across the developed world, not just in the U.S., compared to prior recessions.
When we look at a bunch of models on leading indicators for how severe a recession we might have, it doesn't look anything like 2009, and it looks like a milder version of what we had in 2020. That said, those leading indicators are suggesting a decline in earnings, and so given those weakening leading indicators and what looks like earnings declines, I think we're going to have a rollover in equity markets sometime this fall, closer to the June lows for anybody looking for a better entry point.
We have a whole bunch of charts in here that walk through all of this, but the bottom line is we're coming out of a decade where across the developed world you had financial repression and short rates and long rates, particularly after you adjust for all the quantitative easing that were way below, abnormally below, the returns on financial assets. That gap is now closing which creates less incentive for leverage, less incentive for risk taking, most incentive for a resetting of portfolios to less-risk assets, and I think that process is going to be something where you don't want to be too aggressive as that's taking place.
So, bottom line is looks like a mild recession for the United States is in the cards. Earnings will probably decline. Look for a rollover in the equity markets sometime this fall. Part of that's already happening. Then let's just see how far those leading indicators go down. Of course, the actual wage and consumer price inflation prints over the next few months are going to be really key drivers of just how high rates have to go.
There's a couple of pages of exhibits here. Some of the exhibits that are worth looking at are exhibits on the collapse of new orders versus production, how inventories are extremely elevated, the leading indicator model that we use to look at what earnings are up to, that kind of thing.
Then there's also a table in here, every time the fed has hiked rates since 1965 you've had a recession sometimes, and not other times. When you haven't had a recession, the common factor or at least one of the common factors have been food and energy inflation in single digits of 4-5%. So again, when you haven't had a recession after fed hikes it's happened in those times when food and energy inflation was very low. That's not the case this time around, and that's why I think you've got a one in two chance for recession next year.
Okay, so let's talk a little bit more about the energy bill and why it's so important to try to understand what's going on with it. When there's a bill that affects taxes and spending, the CBO comes out with projections of what they think happens to the deficit, growth, inflation, things like that. There's no government agency to make GHG or climate projections.
When Manchin and Schumer were working on their energy bill they consulted with three outside energy modeling firms to ask them, hey, if we put these policies in place, what are the GHG reductions going to be. I find in all the breathless support for the bill, and I think it's a good bill, I would have voted for it, but for all the articles talking about a 40-45% decline in GHG emissions resulting from this bill, there's not a single article I've seen to talk about the actual assumptions made to get there.
I took a look at the detailed assumptions by one of those modeling teams. These people are very smart, they're very well informed on energy transition dynamics, but the models they build assume perfectly optimal behavior by every business and every individual based on economic incentives.
So, in other words, if it makes sense for somebody to buy an electric car economically, everyone will do it. They ignore the frictional issues related to supply chains for battery and critical minerals. There's limited acknowledgement of the actual interconnection delays of wind and solar power, and the difficulty in siding new transmission to support that wind and solar power.
Notice that House Democrats, by the way, may already block passage of the infrastructure projects siding bill that Manchin was trying to get them to agree to in exchange for his support.
I looked at a long list of our assumptions versus this modeling group's assumptions, and there were some kind of remarkable differences in there. They've got a pace of solar and wind additions that would represent the fastest pace of any kind of electricity generation capacity added in history, and by a wide margin. They have a seven-times increase in the pace of solar installations, 100% EV penetration of sales in 2030 for passenger cars and light trucks.
What's kind of more amazing is a 90% EV share assumed for medium-duty and heavy trucks, even though those don't exist today. They've got a 30% expansion in the transmission grid over the next few years, even though over the last 10 years it's been closer to 5-10%. Anyway, we walk through all the assumptions. Some of the assumptions that we made are similar to theirs. The reason this is so important is, forget about the GHG issue for a minute, if you accept their presumptions, right now natural gas represents about a third of all primary energy consumption in the United States. Under their assumptions it drops to 20% in just eight years, and falls rapidly after 2030.
So, if you believe those assumptions you would already be taking steps today to curtail the viability and profitability of the natural gas industry because you don't need it in the future, so you might as well start putting it in wind-down mode, similar to what's being done with coal and parts of nuclear. Under our assumptions, the primary share for natural gas is only down a couple of percent in 2030, and so you would not take those steps to constrain the growth and viability of the natural gas industry.
So, even more than the GHG emissions, these policy assumptions of how these bills work is really important, because they drive decisions that are going to be made as it relates to a lot of things about which industries are supported and which aren't. If you take a look at what's going on in Europe right now there's and abject lesson in if you get that wrong it's extremely expensive. I'm sure you've seen this, but we have chart in here on what's happening with the energy prices in Europe and how Germany could actually run out of gas this winter depending upon what Russia does with supplies.
Anyway, take a look. I think it's important for all of us to be fluent as possible in the widgets of what drive these GHG assumptions so that we can identify Panglossian articles when they appear on energy.
The last topic for this month's "Eye on the Market" is the other component of the Inflation Reduction Act is $45 billion dedicated for tens of thousands of new IRS enforcement agents. The CBO did score that part of the bill, and they assume a 4:1 return. In other words, 45 billion invested in new agents and they're going to generated around 200 billion of additional revenues over a 10-year period. Not so fast.
Audit rates have come down over the last 10 years, but are still highly skewed towards people with incomes of a million or more. So, let's assume that the audit rate for those earning more than--let's even it out at 400,000. Let's assume that the audit rate goes back up to seven times what it is now and goes all the way back to what it was in 2010. Based on some information from the general accounting office on how much additional revenue you raise from those kind of audits, that would raise about $8-10 billion a year in 2031, which is way below the $35-40 billion estimated by the CBO.
This all sounds like boring IRS math until you think about the implications here, because Treasury Secretary Yellen and the IRS Commissioner are saying don't worry, we're only going to direct these new agents to focus on wealthier taxpayers, but if focusing on wealthier taxpayers only raises, let's say, 20-30% of the projected revenues they're going to have to look much more broadly at a broader group of taxpayers to raise the money that was assumed here by the CBO and the House Ways and Means Committee.
We have some data in here on audit rates by income and how much money you make by auditing people and things like that. I think part of what's driving this initiative is that the Treasury has published a document suggesting hundreds of billions of dollars of a tax gap every year, which is the difference between what should be paid and what is actually paid. I think a lot of those numbers are vastly overestimated and we walk through some of the computational issues as to why that estimate is way overstated.
But look, that's how we're looking at it. Other people look at it differently. The bottom line is whatever the theoretical tax gap is, it looks like these new IRS agents are going to be focusing intently on a broader group of taxpayers involved with partnerships, sole proprietorships, and owners of commercial and residential property. The clue there is there was a chart from the Treasury that they published this year that showed the percentage of income not reported, in other words, underreporting of income.
For people and entities that are subject to information reporting and withholding, they assume almost a zero percent noncompliance rate, and even when there's no withholding and partial reporting, the noncompliance rate is 15%. But where they're really going to be looking is they assume a 55% noncompliance rate for certain kinds of partnerships, proprietorships, and owners of commercial and residential rents and royalties and things like that. So, that really is where it looks like they're going to be focusing here.
We have a couple of pages explaining all of this, and then just to round things out, the IRS also believes that there's a very large degree of noncompliance and nonreporting by crypto holders. There's been a whole bunch of new executive orders focused on that.
There was a widely publicized on Twitter enforcement announcement of someone you will have heard of for tax evasion related to crypto that took place last week, and so that's what we think is going to come next. A lot of comprehensive field exams of digital asset funds, principals, and investors, and some economic and other kinds of penalties that are going to be very well publicized to raise the bar for people that are noncompliant.
If you didn't get a chance to see it, in July in the last "Eye on the Market" we had a great chart on Bitcoin according to Shakespeare, so if you haven't seen that, please take a look. It's a chart with different Shakespeare quotes depending on what the price of bitcoin was actually doing.
So, thank you very much for listening. We are having a Zoom webcast of some kind with Henry Kissinger in September that a lot of you will receive invitations to, to talk about what's going on. Henry's almost 100, so it'll be interesting to hear what he has to say. Thank you for listening. Bye.
FEMALE VOICE 1: Michael Cembalest's "Eye on the Market" offers a unique perspective on the economy, current events, markets, and investment portfolios, and is a production of JP Morgan Asset and Wealth Management. Michael Cembalest is the Chairman of Market and Investment Strategy for JP Morgan Asset Management and is one of our most renowned and provocative speakers. For more information, please subscribe to the "Eye on the Market" by contacting your JP Morgan representative. If you'd like to hear more, please explore episodes on iTunes or on our website.
This podcast is intended for informational purposes only and is a communication on behalf of JP Morgan Institutional Investments Incorporated. Views may not be suitable for all investors and are not intended as personal investment advice or a solicitation or recommendation. Outlooks and past performance are never guarantees of future results. This is not investment research. Please read other important information which can be found at www.JPMorgan.com/disclaimer-eotm.
[END RECORDING]

