Slide Image
Chart Image
Dollar drivers
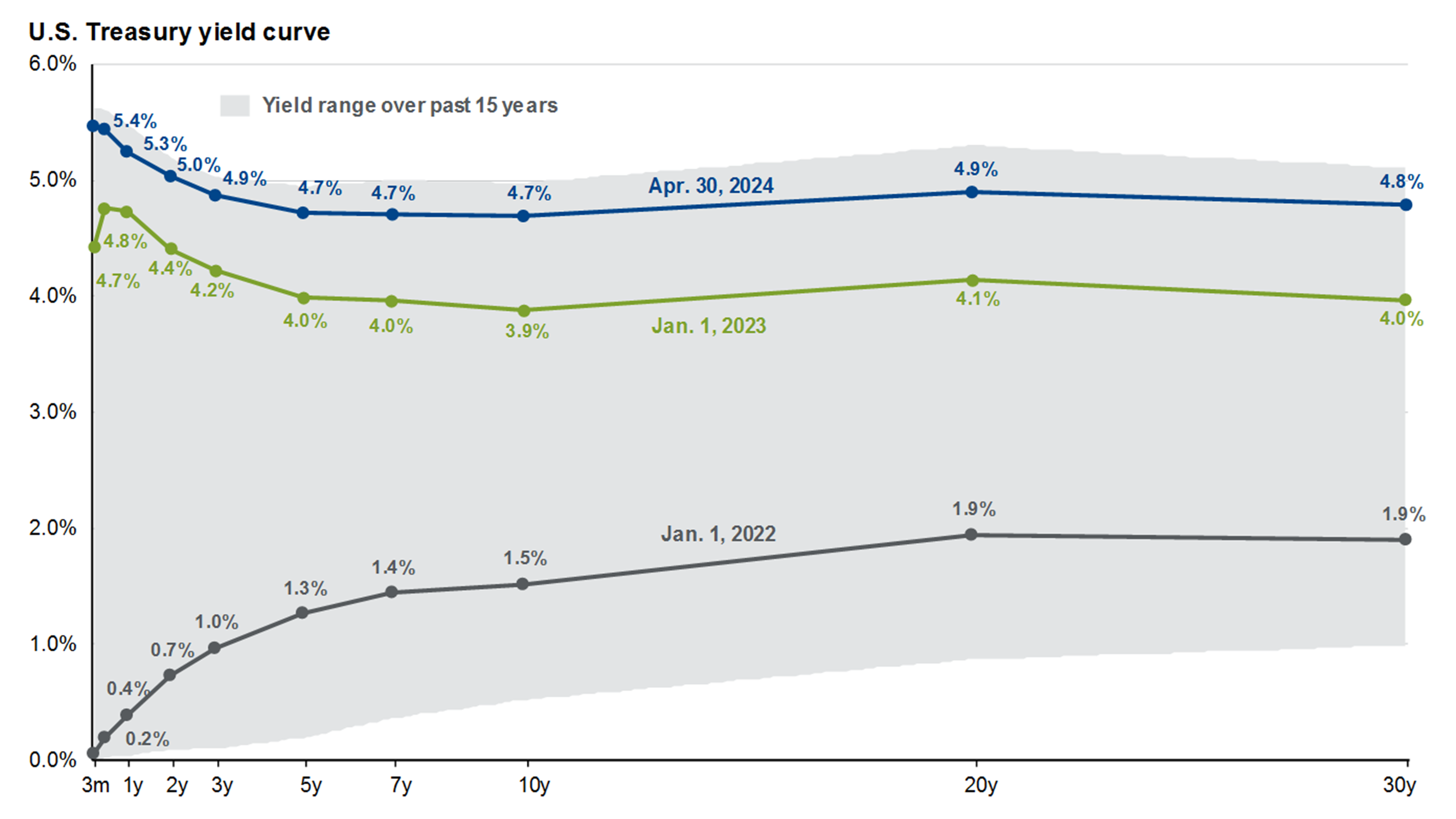
This chart on the left looks at the value the U.S. dollar while the two charts on the right show drivers of the U.S. dollar. The top right chart looks at the long-run driver of the U.S. dollar and shows the current account balance of the U.S. as a percent of GDP. A stronger U.S. dollar tends to lead to a larger current account deficit as a percent of GDP. In the short-run, the U.S. dollar is driven largely by interest rate differentials as shown in the bottom right-hand chart, which compares the 10-year U.S. Treasury yield to a basket of 10-year yields for each major trading partner. Over the long run, we expect that narrowing interest rate differentials and the large U.S. trade deficit will cause the dollar to decline.