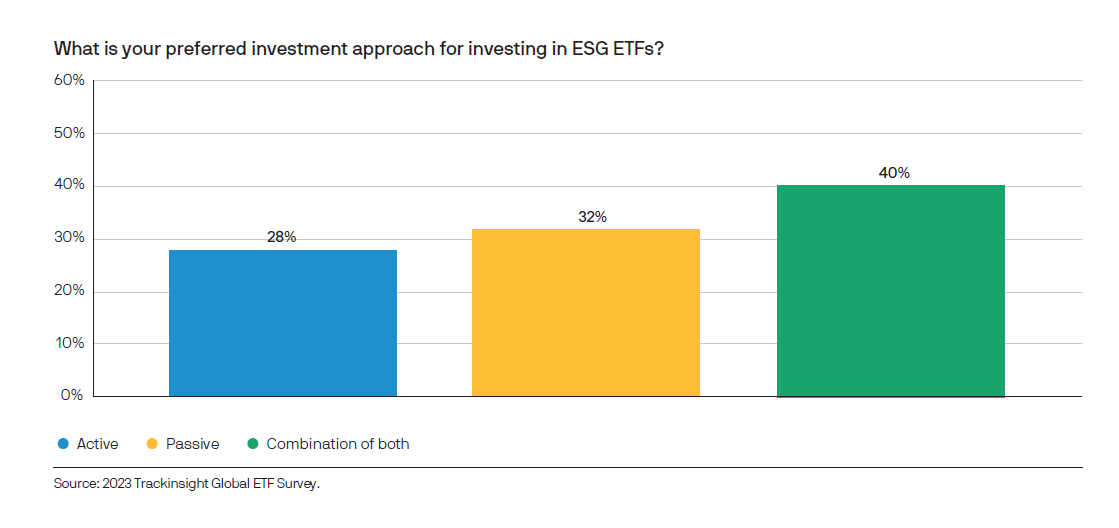
Unlike passive index investing, an active approach allows for a more in-depth assessment of ESG characteristics
While some index trackers use exclusions alone to reflect investors’ sustainability preferences, exclusionary strategies will only help investors mitigate ESG risks by avoiding companies with the worst ESG attributes. As a result, investors who are looking to invest in companies with strong ESG practices, or to capitalise on sustainable opportunities, will need to look beyond exclusions alone.
When it comes to ESG ETFs, combining the benefits of ETFs with active management can be particularly advantageous. Passive ESG ETFs typically apply exclusions or, if a sharper ESG focus is required, they track ESG indices such as socially responsible investment (SRI) or Paris-aligned benchmarks. As a result, investors are fully reliant on the ESG analysis of these index providers.
Expected Change in investment vehicles used to access ESG
09ab221212093730