Slide Image
Natural gas trends
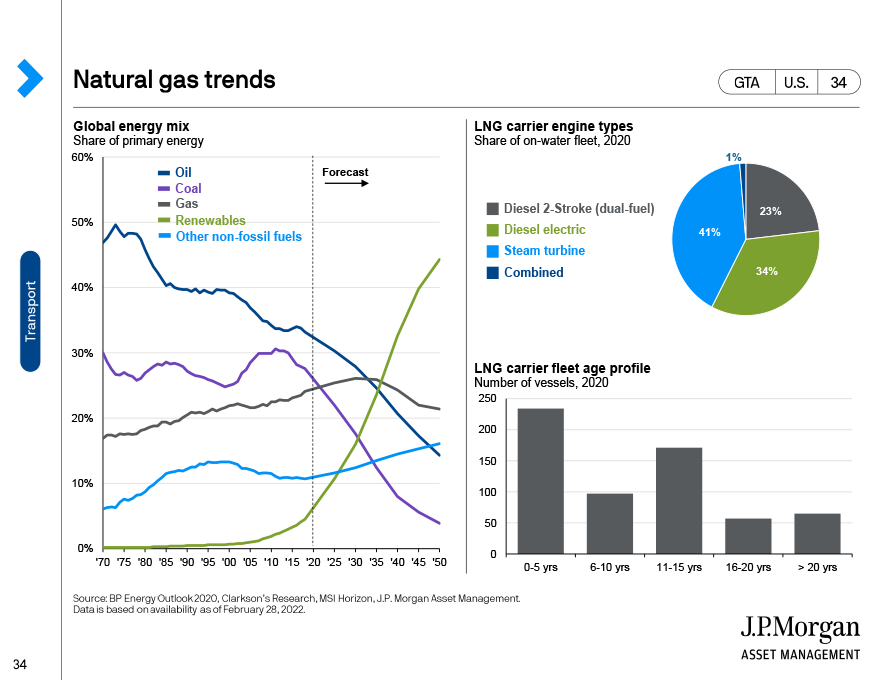
The usage of renewable energy is projected to increase over the next two decades. In the left chart, renewables (green) is forecast to grow from less than 10% of the share of primary energy to over 40%. Other non-fossil fuels are set to rise as well. However, BP estimates that oil, coal, and gas will all decline.
However, this is likely to be a much more gradual transition in reality, and natural gas is still likely to be prominent given its cost efficiency and availability. From a shipping standpoint, this creates a clear opportunity. Nearly 77% of the LNG carrier fleet is outdated, as 2-stroke, dual-fuel engine technology offers up to 60% improvement in fuel efficiency over legacy assets, per the top right chart. Furthermore, nearly 20% of the LNG carrier fleet is more than 15 years old, and current shipyard production capacity limitations are ~50 LNG carriers per year (<20% of current fleet), per the bottom right chart. This dynamic minimizes the risk of asset over-supply in an environment of strong demand.